Architecture summary
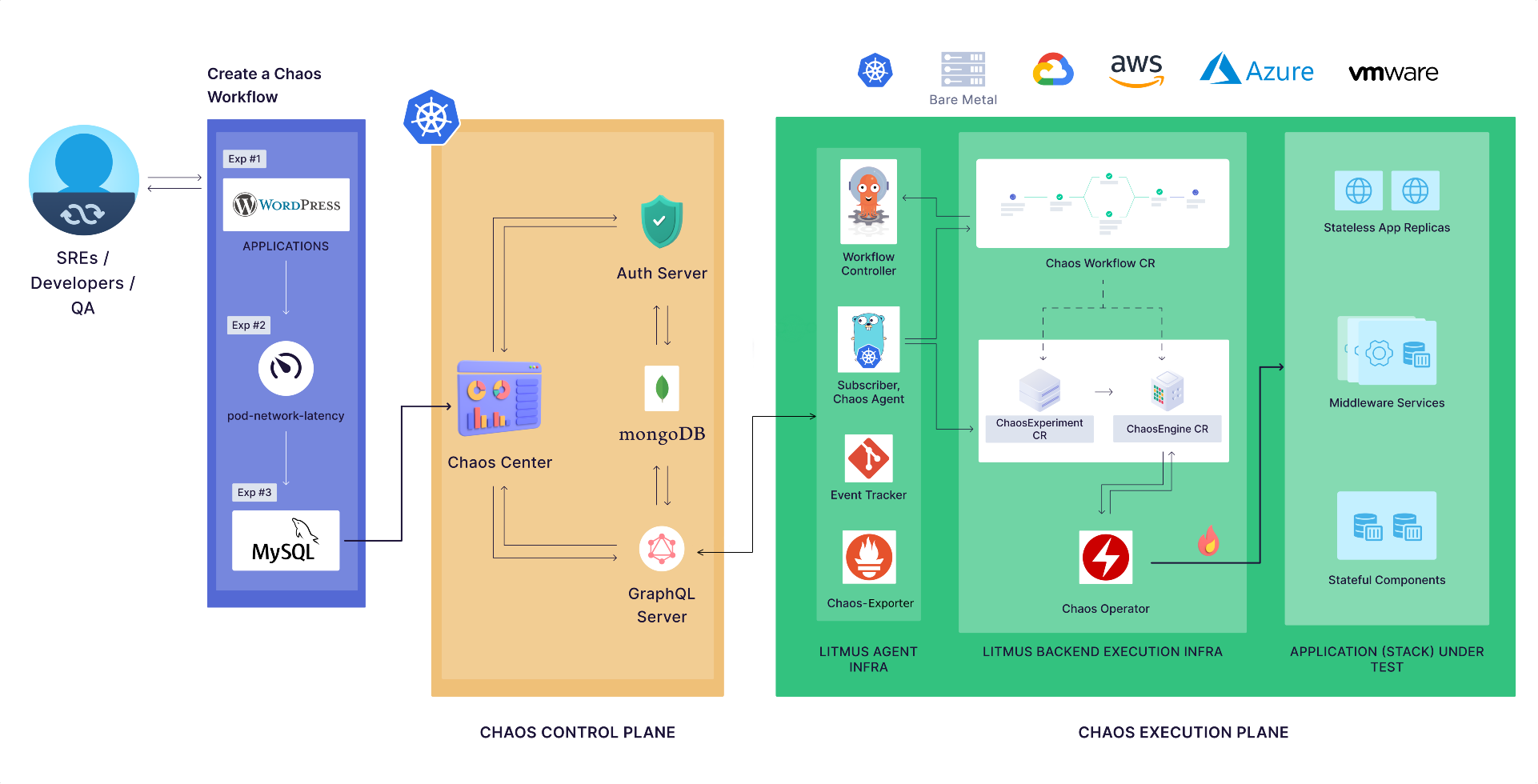
The Litmus architecture can be segregated into two parts:
Control plane: Contains the components required for the functioning of ChaosCenter, the website-based portal for Litmus.
Execution plane: Contains the components required for the injection of chaos in the target resources.
How Litmus works?
Control plane can be used for creating and scheduling chaos experiments, which is a set of chaos faults defined in a definitive sequence to achieve desired chaos impact on the target resources upon execution. Users can log in to the ChaosCenter using the web UI or the APIs to define a chaos experiment and assess the resilience of target workloads.
Once the user creates a chaos experiment using the ChaosCenter, it is passed on to the execution plane. The Execution plane can be present either in the same cluster as the ChaosCenter if the self chaos infrastructure is being used, or in a remote cluster if an external chaos infrastructure is being used. The Execution plane interprets the chaos experiment as a list of actions that will inject chaos into the target workloads. It ensures efficient orchestration of chaos in various cloud-native environments using Kubernetes custom resources.
Once the chaos experiment is executed, Execution plane sends the chaos result to the control plane for their post-processing using either the built-in monitoring dashboard of Litmus or using external observability tools such as Prometheus DB and Grafana dashboard. Litmus also achieves automated chaos experiment runs to execute chaos as part of the CI/CD pipeline based on a set of defined conditions using GitOps.
note
With the latest release of LitmusChaos 3.0.0:
- The term Chaos Delegate/Agent has been changed to Chaos Infrastructure.
- The term Chaos Experiment has been changed to Chaos Fault.
- The term Chaos Scenario/Workflow has been changed to Chaos Experiment.
Refer to the Glossary documentation for more info.