Configuring GitOps
note
With the latest release of LitmusChaos 3.0.0:
Introduction
GitOps enables you to configure a single source of truth for your chaos experiment and faults, any changes made either to the artifacts stored in the configured git repository or the portal will be synced.
Before you begin
- Gitops
- Chaos Infrastructure
- Chaos Experiment
- Ensure that you have an active internet connection and a Git repository.
Steps to configure GitOps
- Setup a hosted Git repository so that the ChaosCenter can sync with it and push all the chaos experiments in that repository.
- The Git repository can be public or private, but for authorization you have to provide an access token or any other mode of authentication.
- Login to ChaosCenter and navigate to GitOps (Project Setup > GitOps on the left nav).
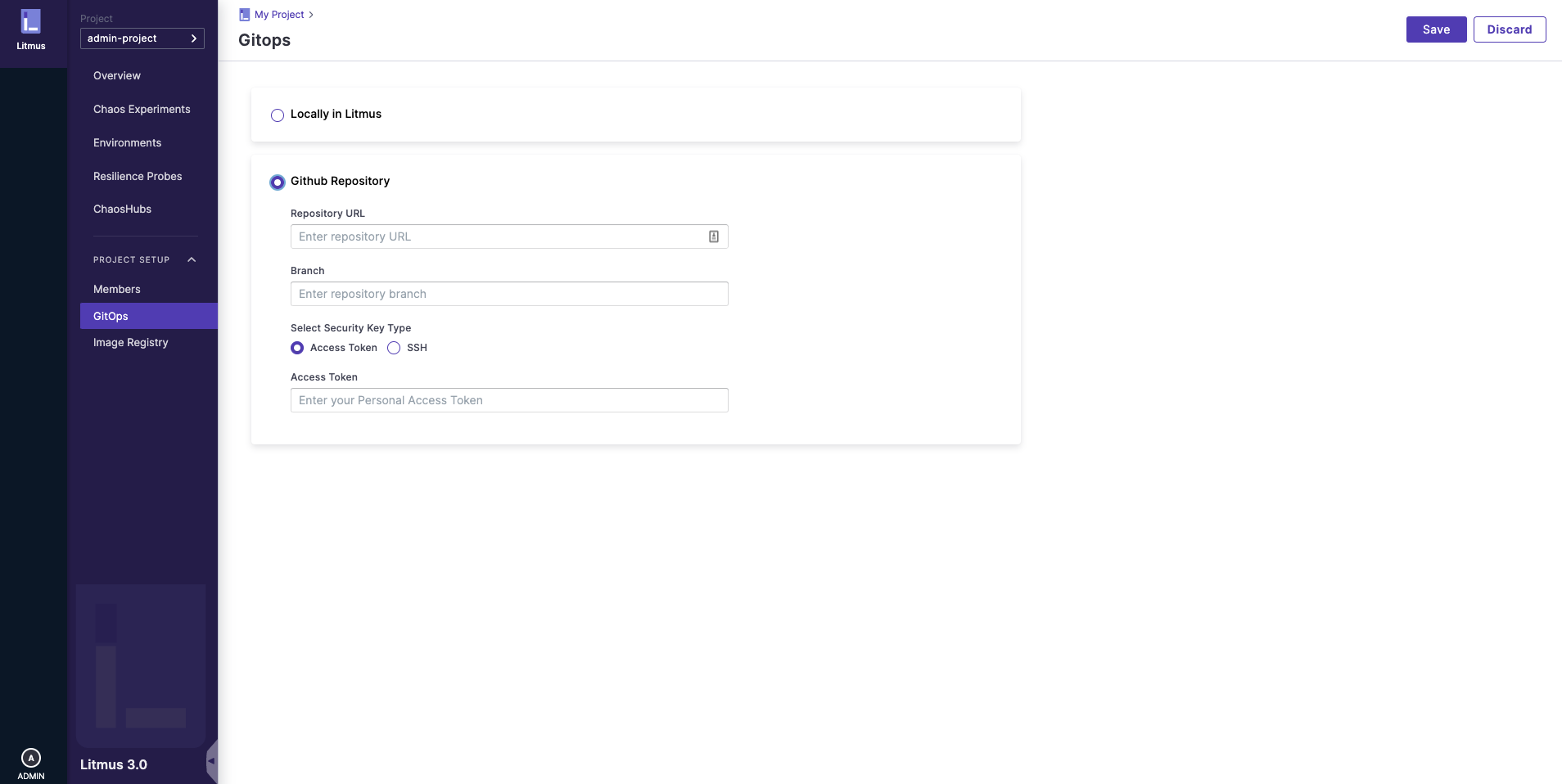
- Select the Git Repository radio button.
- Copy the URL of your Git repository and paste it in the Repository URL input field.
- Enter the branch where you want to sync your chaos experiments.

- You can allow access of your repository either through an access token or through an SSH key.
- In the case of the SSH key, click the button Generate New SSH Key and just copy the key and paste it in the Deploy Keys Tab inside Settings in your Git - repository. Click on the allow write access checkbox, and then on the Add key button.
- Go back to the portal and click on the Save button. A snackbar will pop up showing, Successfully updated GitOps! message.
- Some metadata will be pushed to your repository, that is the ID of your project.
- Now whenever you schedule a chaos experiment, it will automatically be pushed to your repository, and that repository will be the single source of truth.
note
It is also possible to account for the chaos experiments that are created and pushed to the Git repository directly, after configuring GitOps. In this case, if the chaos experiment is a single run chaos experiment, then it starts executing as soon as it is pushed to the repository. Alternatively, if the chaos experiment is a scheduled chaos experiment, then it executes as per the defined schedule. On the other hand, updating an existing chaos experiment present in the Git repository will not execute the chaos experiment but only sync the chaos experiment resource definition with the ChaosCenter, if applicable.
Steps to configure Event-Triggered Chaos Injection
- Once the chaos experiment is pushed to your repository, you’ll notice every chaos experiment has a
experiment_id. You can get this from the chaos experiment YAML file. You need to copy the id and annotate the target application so that if there’s any change in the application, gitops will sync the chaos experiment using this experiment_id and run it on your target application. You can use the following command:
kubectl annotate deploy/target-application litmuschaos.io/experimentId=${experiment_id}
kubectl annotate deploy/target-application litmuschaos.io/gitops=true
- You can check if the event-tracker is running using this command:
kubectl get pods -n litmus -w
- To check the logs copy the pod name of the event-tracker and add it to the following command:
kubectl logs -f event-tracker-pod-name -n litmus
In the logs, you’ll notice that the event-tracker has started. If you make changes in the application the event tracker will trigger the chaos injection. If the policy conditions are met then the event tracker will inform the server to schedule a chaos experiment in that same target. For eg: if you have an Nginx app as your target application, you can just edit the deployment and change its image tag, this will trigger the chaos injection.
Below is a sample policy where two conditions are present and will be validated by the respective operator. The chaos experiment will be triggered if both conditions are met due to the AND condition type.
apiVersion: eventtracker.litmuschaos.io/v1
kind: EventTrackerPolicy
metadata:
name: eventtrackerpolicy-sample
namespace: litmus
spec:
# Add fields here
condition_type: "and"
conditions:
- key: "spec.replicas"
value: "1"
operator: EqualTo
- key: "spec.template.spec.containers[0].image"
value: "nginx:1.18"
operator: EqualTo
Currently supported policy operators are:
- EqualTo
- NotEqualTo
- LessThan
- GreaterThan
- GreaterThanEqualTo
- LessThanEqualTo